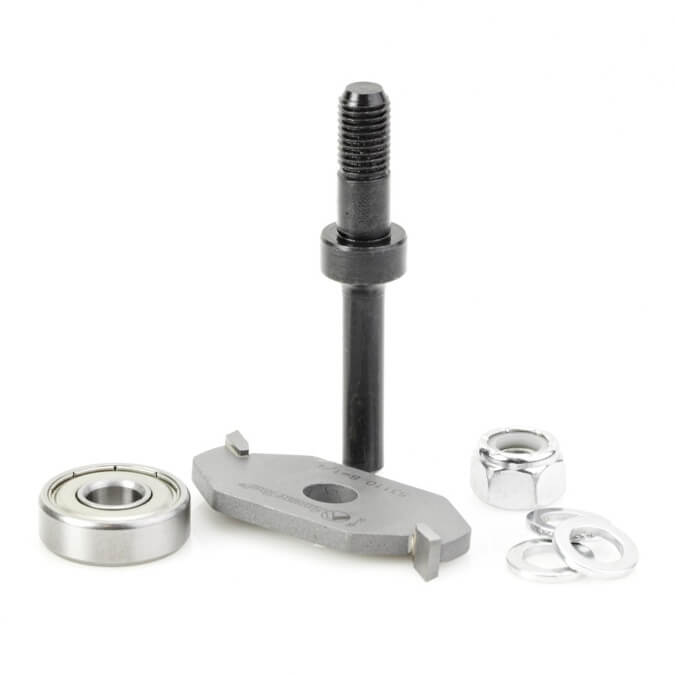
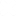
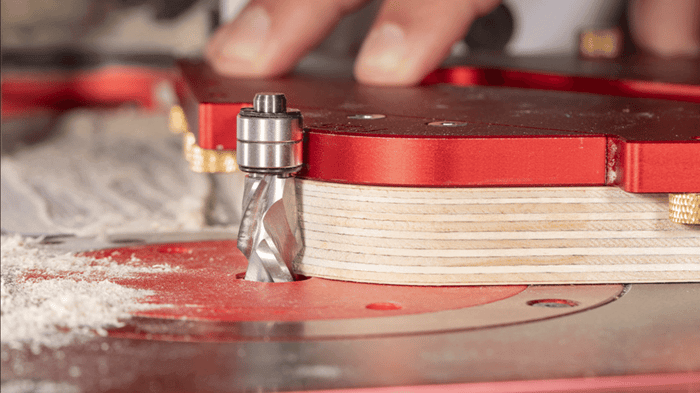
Flattening and Spoilboard Bits for Smooth Surfacing
What Are Flattening and Spoilboard Bits?
Flattening Router Bits
- Purpose: Flattening router bits are designed to level or plane the surface of a workpiece, ensuring it is smooth and even. They are commonly used on wide boards, slabs, or glued-up panels.
- Design: These bits typically feature a large cutting diameter, multiple cutting edges, and a flat bottom, allowing for efficient material removal and a smooth finish. The size of the bit is crucial for covering large areas quickly.
- Application: Ideal for use in router sled setups or CNC machines to flatten and smooth large wooden surfaces. They can be used to remove imperfections, twist, or warp from the wood, providing a flat, even surface ready for further processing.
Spoilboard Router Bits
- Purpose: Spoilboard router bits are used primarily in CNC routing to ensure the spoilboard (a sacrificial board beneath the workpiece) remains flat and level. A flat spoilboard is essential for accurate cutting and engraving.
- Design: These bits are similar to flattening bits but are specifically designed for resurfacing spoilboards. They often have multiple cutting edges and a broad cutting surface to cover large areas effectively.
- Application: Regularly used in CNC machines to maintain a flat spoilboard, which helps ensure consistent depth and accuracy in cuts. Spoilboard bits can also be used to clean up other large flat surfaces.
Key Differences
- Purpose: Flattening bits are focused on the workpiece itself, while spoilboard bits are used to maintain the sacrificial board in CNC setups.
- Usage: Flattening bits are more versatile, often used in both handheld and CNC routers for large surface planing, while spoilboard bits are primarily for CNC applications.
Both types of router bits are essential for achieving flat, even surfaces in woodworking projects, particularly when precision is required.
Why Are Flattening and Spoilboard Bits Important?
Flattening and spoilboard router bits play a crucial role in woodworking, particularly in achieving precision and quality in large surface projects. Here’s why they are important:
Flattening Router Bits
- Ensuring Flat Surfaces: Flattening bits are essential for creating smooth, even surfaces on large workpieces like tabletops, slabs, or panels. This is especially important when working with natural wood, which can often have imperfections, twists, or warps.
- Improving Workpiece Quality: By using a flattening bit, woodworkers can eliminate surface irregularities, leading to a higher quality finish that is ready for further processing, such as sanding, staining, or assembly.
- Saving Time: These bits cover large areas quickly, reducing the time and effort required to achieve a flat surface compared to traditional hand tools or smaller bits.
Spoilboard Router Bits
- Maintaining Accuracy in CNC Work: A flat spoilboard is essential for ensuring that cuts and engravings made by a CNC router are consistent and precise. Spoilboard bits help maintain this flatness, which directly impacts the quality of the final product.
- Prolonging Spoilboard Life: Regular use of a spoilboard bit helps to extend the life of the spoilboard by evenly resurfacing it, preventing dips and grooves that could affect workpiece accuracy.
- Enhancing CNC Efficiency: With a well-maintained spoilboard, CNC machines can operate more efficiently, reducing errors and ensuring that each project is executed with precision.
Overall, flattening and spoilboard bits are indispensable for woodworkers aiming to achieve professional-grade results. Whether it's ensuring a flat, even workpiece surface or maintaining the accuracy of a CNC machine, these tools are vital for quality and efficiency in woodworking.
What Are the Features to Look for in Flattening and Spoilboard Bits?
When selecting flattening and spoilboard router bits for your DIY projects or small manufacturing needs, several key features should be considered to ensure optimal performance and results. Here’s a detailed look at each important feature:
1. Shank Size
The shank size of a router bit refers to the diameter of the part of the bit that fits into the router collet. Common shank sizes include 1/4 inch and 1/2 inch. The choice of shank size affects the stability and precision of the bit during operation:
- 1/4-inch shank: These bits are generally less expensive and suitable for lighter tasks or smaller routers. They can be more prone to deflection under heavy loads, which might affect precision.
- 1/2-inch shank: Bits with a 1/2-inch shank are more robust and offer greater stability and reduced vibration. They are ideal for heavier-duty work and provide more consistent results in larger routers.
When choosing a bit, consider the capabilities of your router and the scale of your projects. A larger shank size generally provides better control and precision, especially for extensive flattening tasks.
2. Cutting Diameter
The cutting diameter of a router bit is the width of the cutting edge and determines the size of the material that can be machined in a single pass. This feature is crucial for both efficiency and the quality of the finished surface:
- Larger cutting diameter: A larger diameter bit can remove more material with each pass, making it suitable for big spoilboard or flattening jobs. It reduces the number of passes required, which can save time.
- Smaller cutting diameter: Smaller diameter bits are typically used for finer work or smaller areas. They are ideal for detailed or intricate patterns where precision is more important than speed.
Choose a cutting diameter based on the size of your workpiece and the level of detail required. Larger bits are preferable for larger surfaces, while smaller bits are suited for detailed work or confined spaces.
3. Cutting Length
The cutting length of a router bit is the distance from the tip of the bit to the end of the cutting edge. It affects the depth of material that can be cut in a single pass:
- Longer cutting length: Bits with a longer cutting length can handle deeper cuts, which is useful for tasks requiring significant material removal or for thicker workpieces.
- Shorter cutting length: These are ideal for shallower cuts and can offer greater stability and control. They are less likely to cause the bit to flex, which can improve precision for finer work.
Consider the thickness of the material you will be working with. If you need to make deep cuts or work with thicker materials, a bit with a longer cutting length will be necessary.
4. Number of Flutes
The number of flutes on a router bit affects the smoothness of the cut and the removal of chips or debris. Flutes are the spiraled grooves that cut into the material:
- Two flutes: Bits with two flutes are generally more aggressive and can remove material more quickly. They are suitable for roughing out large areas or for tasks where speed is crucial.
- Three or more flutes: Bits with three or more flutes provide a smoother finish by creating finer cuts and better chip removal. They are ideal for achieving a high-quality surface finish, particularly on spoilboard surfaces where a smooth final result is desired.
Select the number of flutes based on the desired finish and the type of material. For a smoother finish, especially on visible surfaces, bits with more flutes are advantageous.
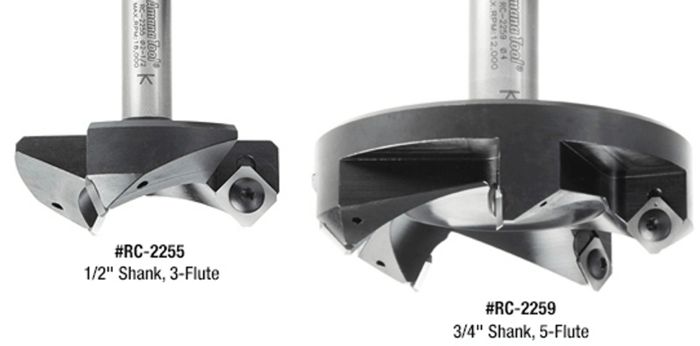
Heavy Duty CNC Insert Carbide Spoilboard 3 & 5 Wing Plunging, Surfacing, Planing, Flycutting & Slab Leveler Router Bits are great for cutting large surface areas and surface planing. Higher number of teeth allows for higher feed rate. These industrial router bits feature solid carbide insert knives with four cutting edges that allow users to rotate the knife when one side becomes dull providing the highest-quality finish available on woodworking tools.
How to Choose the Right Flattening and Spoilboard Bit for Your Project?
Selecting the right flattening and spoilboard bit is crucial for achieving the best results in your woodworking projects. Each project may have different requirements based on the material, the depth of the cut, and the type of finish desired. Here’s how to make the right choice:
1. Consider the Material You Are Working On
The type of material you are working with significantly influences the choice of router bit. Different materials have varying hardness and density, which affects how the bit performs:
- Softwoods (e.g., pine, cedar): For softwoods, a bit with fewer flutes may be sufficient as these materials are easier to cut. However, ensure the bit is sharp to avoid splintering and to achieve a smooth finish.
- Hardwoods (e.g., oak, maple): Hardwoods require bits designed to handle higher stress and heat. Bits with more flutes or those made from high-quality carbide can help manage the extra pressure and provide a cleaner cut.
- Composite materials (e.g., MDF, plywood): For composite materials, which can be prone to chipping and tear-out, a bit with a finer edge and more flutes is beneficial. This helps in achieving a smooth finish and reducing material waste.
Choose a bit based on the material’s characteristics to ensure effective cutting and a clean finish. Understanding the material helps in selecting the appropriate bit type and design.
2. Determine the Depth of Cut Needed
The depth of cut required for your project will determine the appropriate cutting length of the router bit:
- Shallow Cuts: If you need to make only shallow cuts, a bit with a shorter cutting length will suffice. This allows for better control and reduces the risk of the bit flexing, which can impact precision.
- Deep Cuts: For deeper cuts, choose a bit with a longer cutting length. Ensure that the bit is robust enough to handle the increased load without compromising accuracy or causing excessive vibration.
Assess the thickness of your workpiece and the depth of the material removal required. Using the appropriate cutting length will ensure efficient material removal and prevent issues such as overheating or excessive wear on the bit.
3. Choose the Appropriate Bit Type
Different bit types are designed for various applications, so selecting the right type is essential for achieving your desired results:
- Flattening Bits: These bits are specifically designed to level large surfaces quickly. Look for bits with a larger cutting diameter and a robust build to handle extensive material removal efficiently.
- Spoilboard Bits: Spoilboard bits are ideal for cleaning up and flattening surfaces that have been machined. They usually feature a design that minimizes tear-out and provides a smooth finish. Choose bits with multiple flutes for a finer finish or fewer flutes for quicker material removal.
- Compression Bits: These are suitable for materials that are prone to chipping. They cut from both the top and bottom, helping to reduce tear-out and create a smooth surface. Compression bits are particularly useful for plywood and other layered materials.
Consider the specific needs of your project and choose a bit type that aligns with the desired finish and efficiency. Understanding the capabilities of each bit type will help in selecting the best tool for the job.

Amana Tool 45525-5 5-Pack Carbide Tipped Spoilboard Surfacing & Flattening 3-Flute Router Bits - save 10% when ordering 5 or more of select units like Amana router bits and saw blades. See more discount offers.
How to Properly Use Flattening and Spoilboard Bits?
Using flattening and spoilboard bits correctly ensures effective material removal and a smooth finish. Follow these essential steps:
1. Secure the Workpiece and Bit
Ensure the workpiece is firmly clamped or secured on the router table to prevent movement. Also, make sure the router bit is properly installed and tightened in the collet to avoid any wobbling during operation.
2. Set the Appropriate Speed and Feed Rate
Adjust the router to the recommended speed for the bit and material. A higher speed is generally used for softer materials, while a slower speed works better for harder materials. Set the feed rate according to the bit and material to ensure smooth cutting and avoid overheating.
3. Make Multiple Passes for Best Results
For optimal results, make multiple shallow passes rather than a single deep cut. This approach reduces strain on the bit, improves surface finish, and minimizes the risk of material tear-out or burning.
Differences Between Spoilboard Bits, Flattening Bits, and Flycutters
Understanding the differences between spoilboard bits, flattening bits, and flycutters can help you select the right tool for your woodworking or machining needs. Here’s a breakdown of each tool:
Spoilboard Bits
Description: Spoilboard bits are designed specifically for cleaning up and leveling the surface of a spoilboard, which is the sacrificial layer on a CNC machine or router table. They usually have multiple flutes and a wide cutting diameter to cover large areas efficiently.
Usage: These bits are used to remove material that has been cut or to prepare the surface for future work. They help maintain a flat, even surface by removing imperfections and debris.
Name Origin: The term "spoilboard" comes from the idea that this board is intentionally “spoiled” or worn down to protect the more valuable workpieces and maintain a level surface.
Flattening Bits
Description: Flattening bits are designed to quickly and efficiently flatten large, uneven surfaces. They often have a large cutting diameter and a robust design to handle significant material removal.
Usage: These bits are ideal for leveling rough surfaces, such as those found in slabs of wood, and are commonly used in woodworking projects where a smooth, level surface is required.
Name Origin: The name "flattening bit" directly reflects the tool’s primary function: to flatten or level surfaces.
Flycutters
Description: Flycutters are cutting tools used primarily in milling machines. They feature a single cutting edge or multiple cutting edges on a rotating body and are designed to take large cuts in a single pass.
Usage: Flycutters are used to achieve a smooth finish on metal surfaces or to remove material rapidly. They are typically used in industrial machining for precision work.
Name Origin: The term "flycutter" comes from the tool’s resemblance to a flying object or its ability to cut quickly and efficiently, reminiscent of the fast-moving wings of a fly.
Each of these tools serves a specific purpose based on the type of material and the desired finish, and their names reflect their primary functions and characteristics.